" CALCULATION NOS OF LABOUR
REQUIRED FOR CONSTRUCTION OF
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING "
REQUIRED FOR CONSTRUCTION OF
RESIDENTIAL BUILDING "
ALL ESTIMATION GUIDED BY 'A'
'A' = Plinth Area Per Floor
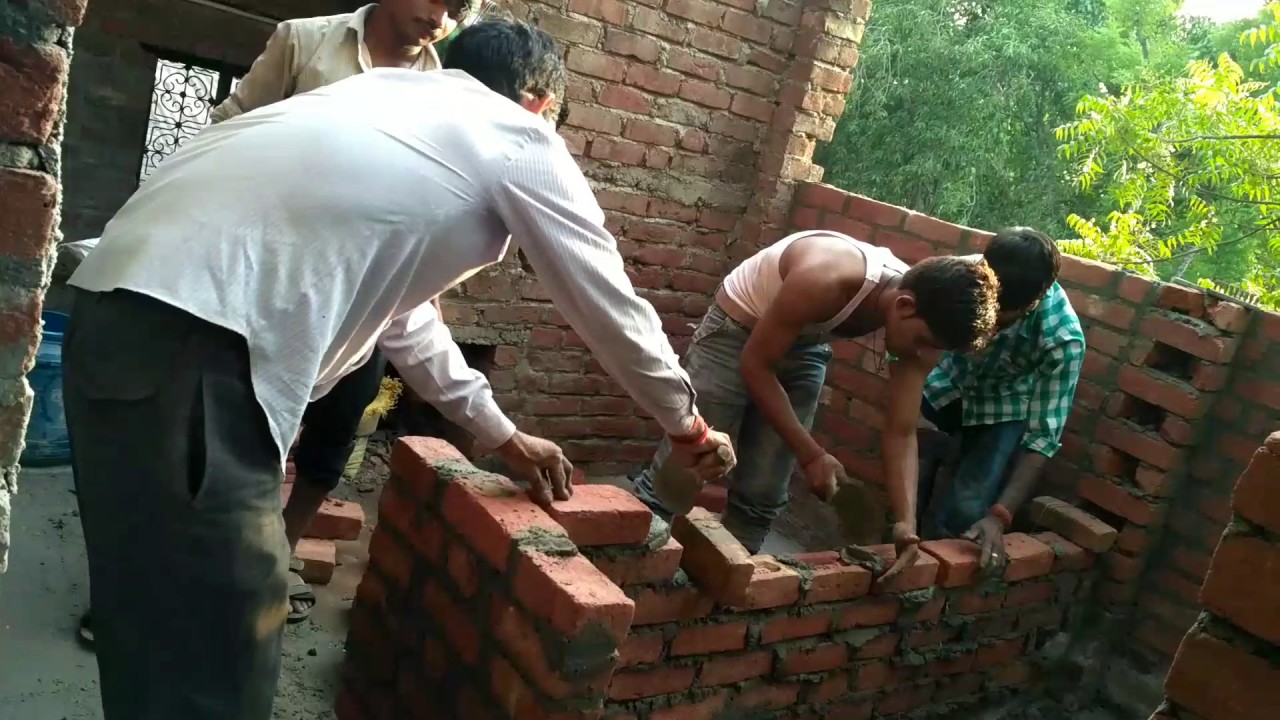
NO OF MASON UNIT IN DAY(TIME)
8 HRS = 1 DAY
A. FOR SINGLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (1.335A + 28)
Labour Required in Day = (1.335A + 28)
B. FOR DOUBLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (1.335A + 6)
Labour Required in Day = (1.335A + 6)
C. FOR FOUR STOREY BUILDING (Framed):
Labour Required in Day = (1.593A - 2)
Labour Required in Day = (1.593A - 2)
2. CARPENTER:
A. FOR SINGLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (1.184A - 9)
Labour Required in Day = (1.184A - 9)
B. FOR DOUBLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (1.194A - 9)
Labour Required in Day = (1.194A - 9)
C. FOR FOUR STOREY BUILDING (Framed):
Labour Required in Day = (1.66A)
3. PAINTER:
Labour Required in Day = (1.66A)
3. PAINTER:
A. FOR SINGLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
B. FOR DOUBLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
C. FOR FOUR STOREY BUILDING (Framed):
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
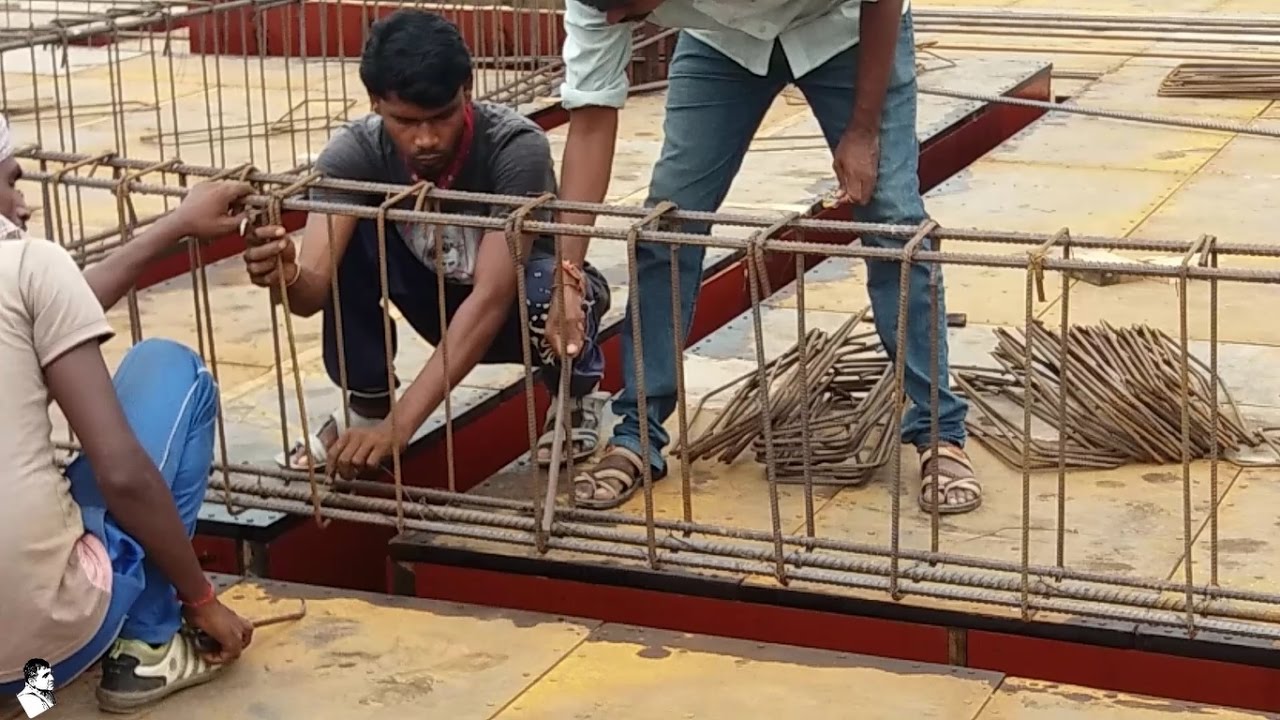
4. BLACKSMITH:
Labour Required in Day = (0.19A)
4. BLACKSMITH:
A. FOR SINGLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (0.269A - 4)
Labour Required in Day = (0.269A - 4)
B. FOR DOUBLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (0.274A - 1.4)
Labour Required in Day = (0.274A - 1.4)
C. FOR FOUR STOREY BUILDING (Framed):
Labour Required in Day = (1.11A - 0.0043A^2 -17.6)
5. MAZDOOR:
Labour Required in Day = (1.11A - 0.0043A^2 -17.6)
5. MAZDOOR:
A. FOR SINGLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (4.769A + 32)
Labour Required in Day = (4.769A + 32)
B. FOR DOUBLE STOREY BUILDING (Load Bearing):
Labour Required in Day = (4.91A + 13)
Labour Required in Day = (4.91A + 13)
C. FOR FOUR STOREY BUILDING (Framed):
Labour Required in Day = (5.833A - 9.2)
Labour Required in Day = (5.833A - 9.2)